Home > Technical Support > Molding Technology > Molding Technology for TOPAS(R) COC
Mold design
7. Mold design 7.2 Gates (1) Gate size More stable products can be molded by positioning the gate at a thick portion of the products. The gate should be sized according to the product shape so as to avoid stress concentration at the gate area. Gate type can be a generally-used side gate, fan gate, and so on. Set sprues and runners on the large side to improve pressure transmission to products.
If there are no quality problems, attach a smaller gate to improve molding cycle, gate finish, etc. Also, if molded products are thin-walled (0.3 mm or less), make thickness equal to molded products to prevent pressure loss of resin.
(2) Gate position
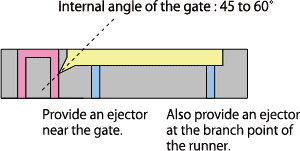
(3) Gate shape Commonly-used gates can be used for TOPAS® COC, which does not have any special trouble with gate shape. However, in the case of a submarine gates, gates may break depending on the shape. Fig. 7-4 shows points to be noted.
Fig. 7-4 Points to be noted for submarine gates
|