Home > Technical Support > Molding Technology > Molding Technology for DURACON(R) POM
Mold Design / Mold Temperature Control
8. Mold Design
8.6 Mold Temperature Control
Since mold temperature has a strong influence on the molding cycle and the quality of molded parts, the method of controlling mold temperature must be investigated beforehand as carefully as other parameters of mold design, such as runners, gates, and knockout methods. The following points should be considered in the design of mold temperature control:
- A hot water circulation system is more favorable than a system employing heaters.
- Points of hot water circulation system:
(a) Provide sufficient heat transfer area for mold cooling channels (many wide cooling channels).
(b) Bring the cooling channel as close as possible to the cavities. (If the cooling channel is far from the cavities, surface temperature distribution becomes wide.)
(c) Provide a sufficient quantity of circulation water. (Use a temperature controller which pumps a large volume and has a pumping pressure that exceeds the pressure loss in the water channel.)
- Consider the employment of core cooling. (Since heat tends to accumulate in the core section, a long molding cycle is required if cooling is not sufficient.)
(a) Water-cooling examples are shown in Figs. 8-6 and 8-7.
(b) Air-cooling example is shown in Fig. 8-8.
(c) Cooling by good heat-conductivity metal is shown in Fig. 8-9.
(d) Cooling by heat pipe is shown in Fig. 8-10.
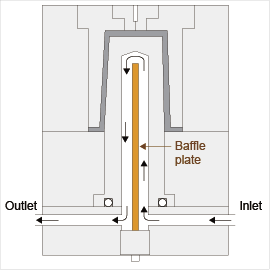
Fig. 8-6 Water-cooling with baffle plate |
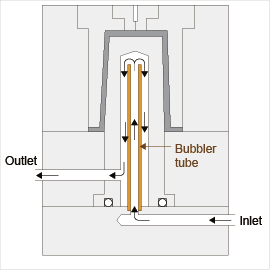
Fig. 8-7 Water-cooling with bubbler tube |
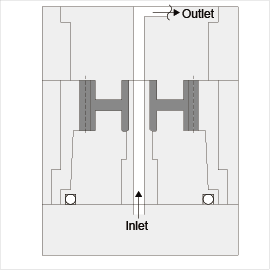
Fig. 8-8 Air-cooling |
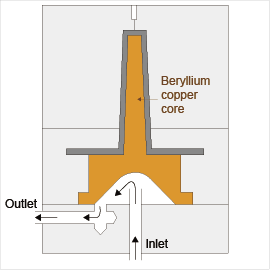
Fig. 8-9 Using good heat-conductivity metal
like beryllium copper |
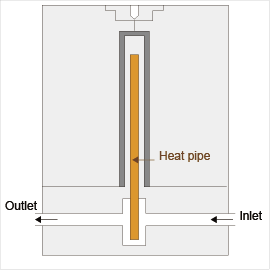
Fig. 8-10 Using heat pipe |
|
|






