Home > Technical Support > Molding Technology > Molding Technology for DURACON(R) POM
Molding Characteristics / Thermal Stability
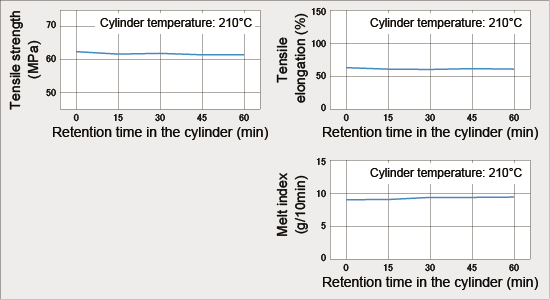
6. Molding Characteristics 6.4 Thermal Stability 6.4.1 Changes in Properties by Holding
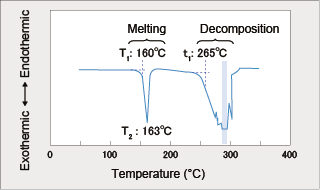
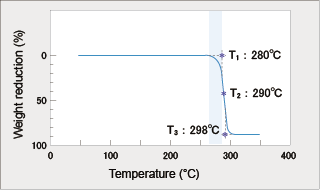
6.4.2 Decomposition Temperature The decomposition temperatures measured by DSC (Differential Scanning Calorimetry) and TG (Thermogravimetry) are shown in Figs. 6-17 and 6-18. These temperatures are 20-30°C higher than that of acetal homopolymer and the melting point is 10°C lower than that of acetal homopolymer. Therefore, the results show that the moldable temperature range of DURACON® POM is wider than that of acetal homopolymer.
|