Home > Technical Support > Molding Technology > Molding Technology for DURANEX(R) PBT
Mold Shrinkage
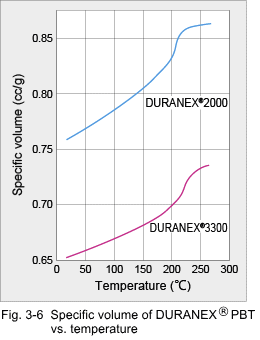
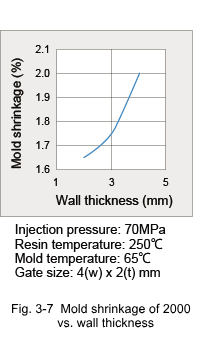
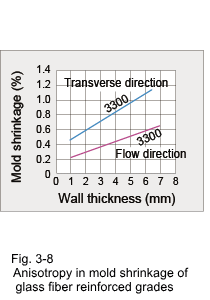
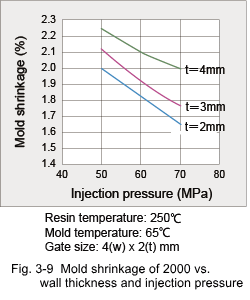
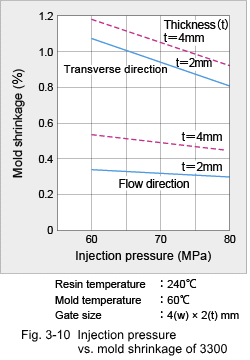
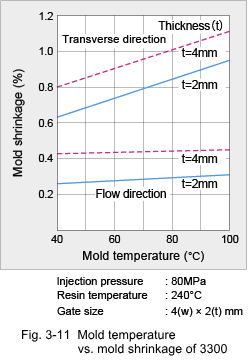
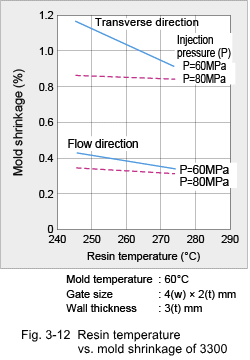
3.2 Shrinkage Characteristics (1) Mold Shrinkage Being a crystalline plastic, the specific volume of DURANEX® PBT varies with temperature as shown in Fig. 3-6. Therefore, mold shrinkage of unreinforced grades is rather high as shown in Fig. 3-7. On the other hand, while reinforcement with glass fiber reduces the mold shrinkage, it also introduces anisotropy in shrinkage because the glass fibers become oriented to the flow direction in the cavity. Some examples of anisotropy in mold shrinkage are shown in Fig. 3-8. Such large anisotropies can cause deformation of molded parts. Key countermeasures to prevent deformation are product shape and gate designs. Mold shrinkage is influenced by molding conditions as shown by the examples in Fig. 3-9, 10, 11 and 12.
|