Home > Technical Support > Molding Technology > Molding Technology for DURANEX(R) PBT
Flowability
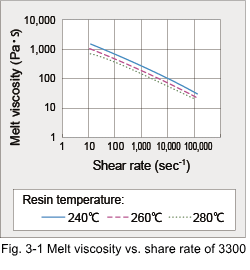
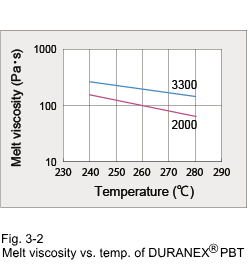
3.1 Flowability The melt index is frequently used as a convenient means of quality control. However, the basic flow characteristics of a material is the melt viscosity. Bar flow length and its L/t (flow length/thickness) ratio are useful parameters for practical molding operations. The relation between shearing stress and shear rate of DURANEX® PBT 3300, when tested with a capillary rheometer, is shown in Fig. 3-1. This relationship is fundamental when designing runners and investigating material flow in cavities. The variation of melt viscosity of DURANEX 2000 and 3300 by temperature is shown in Fig. 3-2. The melt viscosities of 3300 resemble to those of DURACON® POM M90, which means that 3300 has good flow characteristic as a material reinforced with 30% glass fiber.
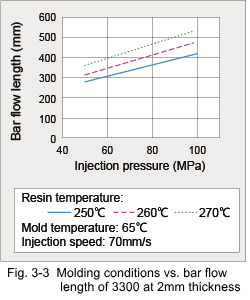
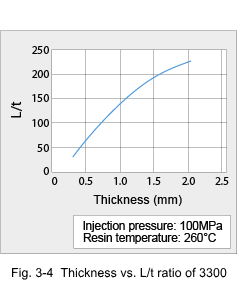
The aforementioned isothermic flow data alone are not sufficient for correct evaluation, because material flow in cavities is not isothermic. In general, it is also difficult to reproduce pressures and shear rates applied in the practical injection molding process in the above-mentioned test apparatus. Therefore, bar flow length tests are carried out on injection molding machines. As an example, the effect of molding conditions on bar flow length of 3300 is shown in Fig. 3-3. Another way to express flow property is the L/t ratio (flow length / thickness). Fig. 3-4 shows L/t ratio of 3300 at the 260°C resin temperature and 100MPa injection pressure. For example, the fact that the flow length reaches around 30mm at a thickness of 0.5mm, indicates the possibility of molding thin sections if sufficient consideration is given to gate design.
|