Home > Products > DURANEX(R) PBT
DURANEX(R)PBT Flame and Hydrolysis Resistant Grade 750AM
Introducing DURANEX® PBT New Grade 750AM Commentary on anti-warpage mechanisms and |
| 1. What causes warpage in PBT |
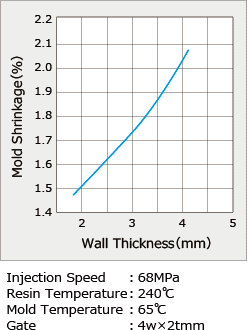
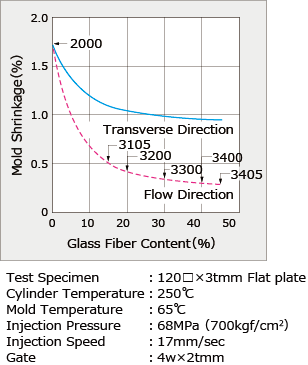
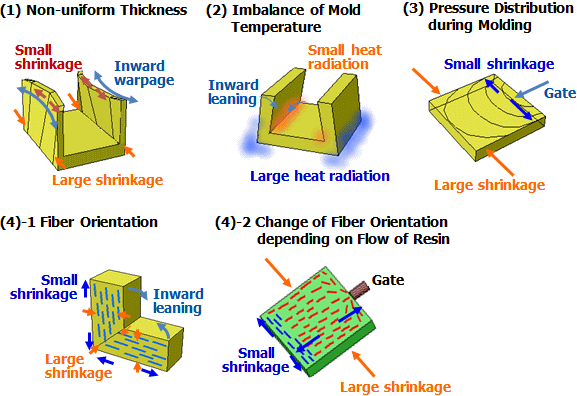
Thermoplastic resins are largely divided into either crystalline or amorphous resin. Crystalline resin has superior mechanical properties, heat resistance, chemical resistance, and other such attributes, but tends to experience larger warpage during molding. Amorphous resin has high transparency and good warpage but tends to be inferior in areas such as chemical resistance. The reason that crystalline resin is prone to warpage is related to its large dimensional change (shrinkage rate) from crystallization. It would seem that warpage would not occur if shrinkage is uniform even with a large shrinkage rate, but shrinkage rate within the molded article actually tends to be uneven, which results in warpage. When crystalline resin solidifies, it will crystallize and shrinkage rate will increase if slowly cooled, but if quickly cooled it will not crystallize and shrinkage rate will be small. When molded articles have more thickness, shrinkage rate will be larger because they cool slowly. However, if the articles are thin they will cool quickly, causing lower shrinkage rate (Figure 1, Figure 3-(1)). Similarly, if the temperature of the mold is high, cooling will also be slow, which means that shrinkage rate will be larger (Figure 3-(2)). Also, the way pressure is applied during molding can change, and shrinkage rate can become uneven due to differences in pressure loss from gate size, flow distance, or other factors (Figure 3-(3)). Additionally, glass fiber reinforcement can have a large effect depending on the fiber orientation. Shrinkage rate is low in the direction of the fiber orientation and larger at a right angle to the fibers (Figure 2, Figure 3-(4)-1). The orientation of the fibers changes according to the flow of resin inside the cavity (Figure 3-(4)-2). These differences in shrinkage rate cause warpage. Since PBT is a crystalline resin, it is a resin with larger warpage. Causes of warpage in injection molded articles can be summarized in the following four points. (1) Shrinkage rate difference due to uneven thickness of products (crystallization) (2) Shrinkage rate difference due to uneven mold temperature (crystallization) (3) Shrinkage rate difference due to pressure difference in the cavity (pressure) (4) Shrinkage rate difference due to shrinkage rate anisotropy from the effect of fiber orientation (reinforcing effect) |
 |
 |
|---|---|
| Fig.1 : Thickness Dependancy of Shrinkage Rate of Non-reinforced PBT | Fig.2 : Glass-fiber Content VS. Molding Shrinkage |
 |
|---|
| Fig.3 : Causes of Warpage Deformation |
2. How DURANEX® PBT achieves low warpage |
|
The three main methods for producing low-warpage materials are as follows. (1) Use low anisotropic filler to reduce anisotropy of shrinkage rate The anisotropy of shrinkage rate can be reduced by using spherical and plate-like fillers with low aspect ratios rather than fiber fillers. This reduces warpage, but on the other hand mechanical strength will also decline. (2) Reduce the absolute value of shrinkage rate by forming alloys with amorphous materials The absolute value of shrinkage rate can be reduced by forming alloys with amorphous resins such as PC and SAN. This method results in little reduction of mechanical strength, but on the other hand the amorphous resin also has an effect on thermal properties and other factors. (3) Improve flowability and reduce uneven pressure distribution Reducing pressure distribution (shrinkage rate distribution) inside the cavity can be expected to produce a certain level of effect on warpage, though not as much as the low-warpage effects of (1) and (2) above. |
3. Main low-warpage grades of DURANEX® PBT |
|
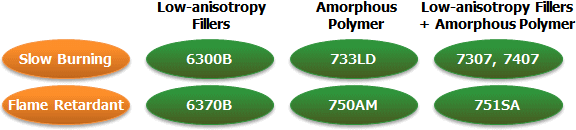
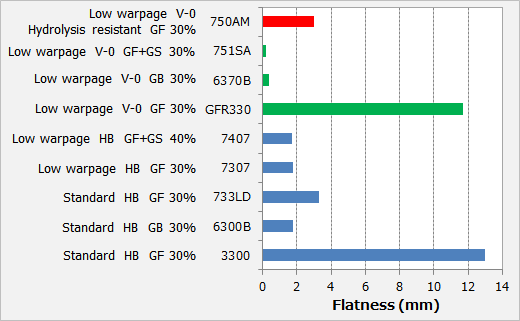
Combining the methods described above, DURANEX® PBT offers a lineup of low-warpage grades with various characteristics (See Figure 4). The physical properties and warpage ratings of each grade are as shown in Table 1 and Figure 5. |
 |
|---|
| Fig.4 : Major Low-warpage Grades of DURANEX® PBT |
 |
|---|
| Fig.5 : Flat Plate (120×120×2mmt) Surface Flatness of DURANEX® PBT Low-warpage grades |
Table.1 : Characteristics of DURANEX® PBT Low-warpage Grades (Full size) |
Mechanical Properties |
ISO Method |
Unit |
3300 |
6300B |
733LD |
7307 |
7407 |
GFR330 |
6370B |
751SA |
750AM |
Tensile Strength |
527-1,2 |
MPa |
140 |
55 |
139 |
106 |
117 |
129 |
47 |
99 |
135 |
Tensile Strain at Break |
527-1,2 |
% |
2.2 |
5.0 |
2.0 |
2.8 |
2.5 |
1.9 |
1.8 |
1.8 |
1.6 |
Flexural Strength |
178 |
MPa |
220 |
91 |
180 |
168 |
180 |
202 |
84 |
149 |
179 |
Flexural Modulus |
178 |
MPa |
9,030 |
3,900 |
9,000 |
6,500 |
9,500 |
10,670 |
4,360 |
8,680 |
9,900 |
Charpy Impact Strength |
179/1eA |
kJ/m2 |
10.5 |
2.0 |
7.6 |
8.0 |
8.8 |
7.1 |
1.9 |
4.6 |
6.5 |
Flammability |
UL94 |
- |
HB |
HB |
HB |
HB |
HB |
V-0 |
V-0 |
V-0 |
V-0 |
4. New flame retardant, low-warpage grade DURANEX® PBT 750AM |
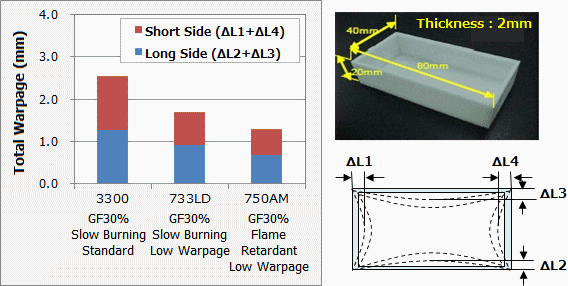
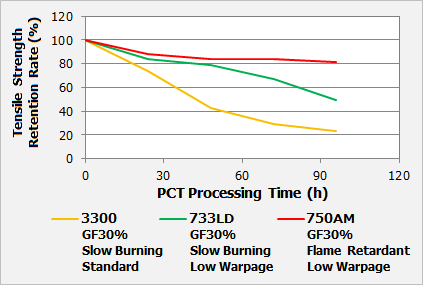
PBT has an excellent balance of mechanical, electrical, and other properties, and when reinforced with glass fibers in particular it delivers dramatic improvements in strength, rigidity, and heat resistance. Since flame retardant can be added to make it flame-proof, PBT is widely used in a variety of industrial products in the electrical and electronic fields. Flame-retardant materials have also been desired recently in the automotive field for use in communication devices and high-pressure parts of EVs and HEVs, and these materials also need to have the high durability and outstanding formability that are required in the automotive industry. DURANEX 750AM is a new GF30% reinforced grade that is flame retardant, low-warpage, and has also been imparted with heat and moisture resistance (hydrolysis resistance). Figures 6 and 7 show the low warpage and the heat and moisture resistance of DURANEX 750AM respectively. We believe it is an ideally suited material for applications such as communication devices and parts for EVs and HEVs, which also has plenty of the durability required in the automotive field. |
 |
|---|
| Fig.6 : Warpage Deformation of DURANEX® PBT 750AM (Evaluation of inward warping of box-type molded object) |
 |
|---|
| Fig.7 : Heat and Moisture Resistance of DURANEX® PBT 750AM (Evaluation of retention rate of tensile strength by PCT) |
5. Conclusion |
PBT is a resin with an outstanding balance of mechanical, electrical, and other properties, but since it is a crystalline material it can present warpage problems during molding. We hope this summary of what causes warpage in PBT and how to counteract it will be useful when you are developing products and designing parts. Also, DURANEX 750AM is a new grade that has the outstanding electrical properties traditionally found in PBT, while at the same time offering low warpage, high rigidity, flame retardance, and hydrolysis resistance. In addition to electrical and electronic parts, we believe it can be useful for parts applications in many different fields including automotive. |
[Related information] • DURANEX® PBT 532AR delivers alkali stress cracking resistance properties |
Technical data sheet is available online: |
◆750AM ◆531HS ◆552HS ◆733LD |
For inquiries about our technologies |
◆Polyplastics Group Representative |
| ◆WEB Inquiry |
26th September 2019 |

