Home > Technical Support > Molding Technology > Molding Technology for DURACON(R) POM
Mold Design / Runners
8. Mold Design 8.1 Runners 8.1.1 Cold Runners (a) Cross-section of runners A round cross-section runner is the most advantageous type, but grooves must be machined in both the stationary and movable platens. If a round runner cannot be used, a trapezoidal runner is recommended. Avoid semi-round runners. An example trapezoidal runner is shown in Fig. 8-1.
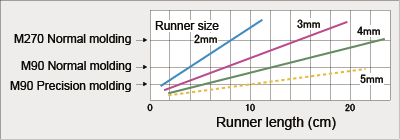
(b) Runner size Although a wide runner is advantageous in terms of preventing material cooling and pressure loss, the runner size is determined in consideration of economic aspects such as setting acceptable runner / cavity ratio to reduce material usage. Fig. 8-2 is a diagram for simplified runner design. This figure shows that required runner diameter can be estimated from the longest runner length. This figure serves as a guide for runner size.
(c) Runner lay-out A multi-cavity mold is designed with equal runner lengths and runner sizes so that the resin fills all the cavities simultaneously, and runners are laid out symmetrically. Example runner lay-outs are shown in Fig. 8-3. When runner lengths to cavities are not equal, or when cavity volumes differ in family molding, the runner size is adjusted for simultaneous filling.
8.1.2 Hot Runners Although the use of hot runners results in advantages such as saving in material and automation of the molding process, it also causes problems such as pressure loss at the hot tips, discoloration at the hot tips and manifold areas, problems in color change, and wider mold temperature. Therefore, the issue of whether or not hot runners should be used must be decided after due consideration of the above concerns. When hot runners are introduced, problems include degating(stringiness), clogging of the gate, drooling, discoloration during retention time and balance among hot tips. The hot runner type should be selected in consideration of these problems. In general, hot runners can be applied to DURACON® POM without problems.
|